
Why Sustainability?
Sustainability is “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
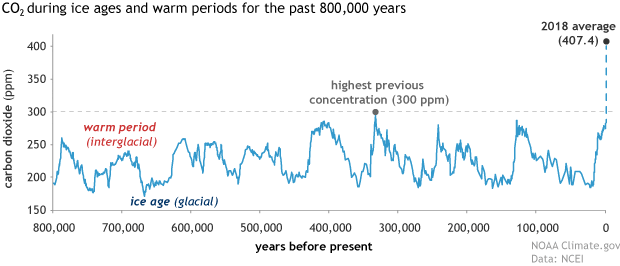
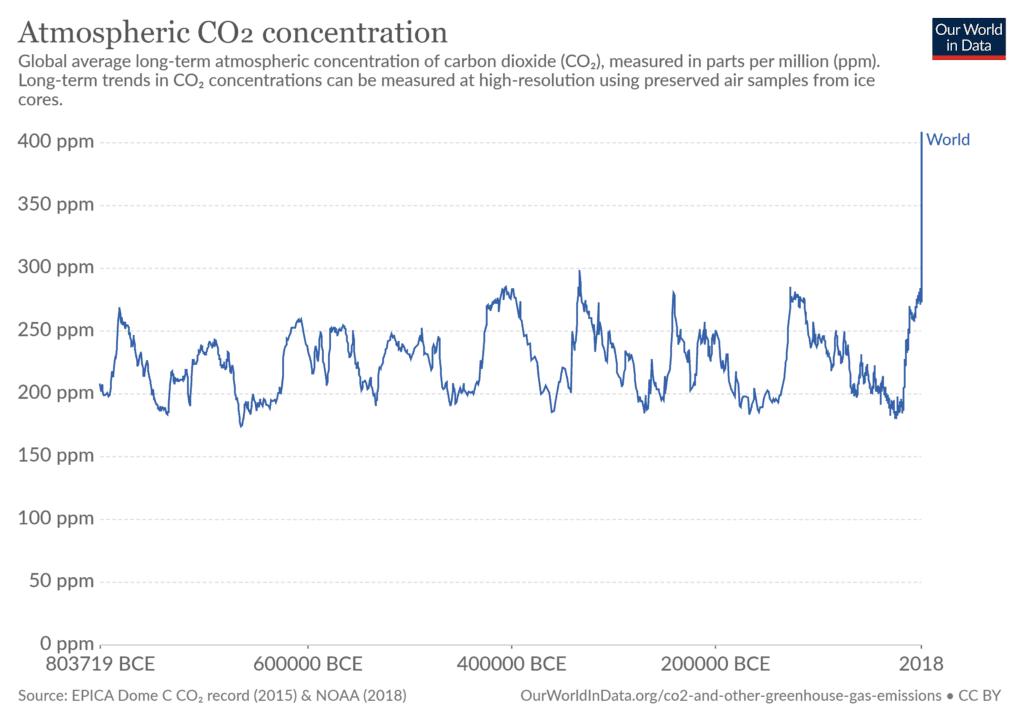
Figure2: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide
The climate emergency is a threat to all species on earth, including humanity. It is exacerbating the rate of biodiversity loss and has resulted in the unfolding of the sixth mass extinction: the Anthropocene.
With rapidly growing urban areas and global population size of approximately 7 and a half billion people, our consumption rates are increasing exponentially. We are depleting Earth’s resources, rapidly resulting in an environmental and ecological emergency.
The exponential growth of the human population means that the increased consumption rates are pressurising ecosystems and exceeding their functional thresholds.
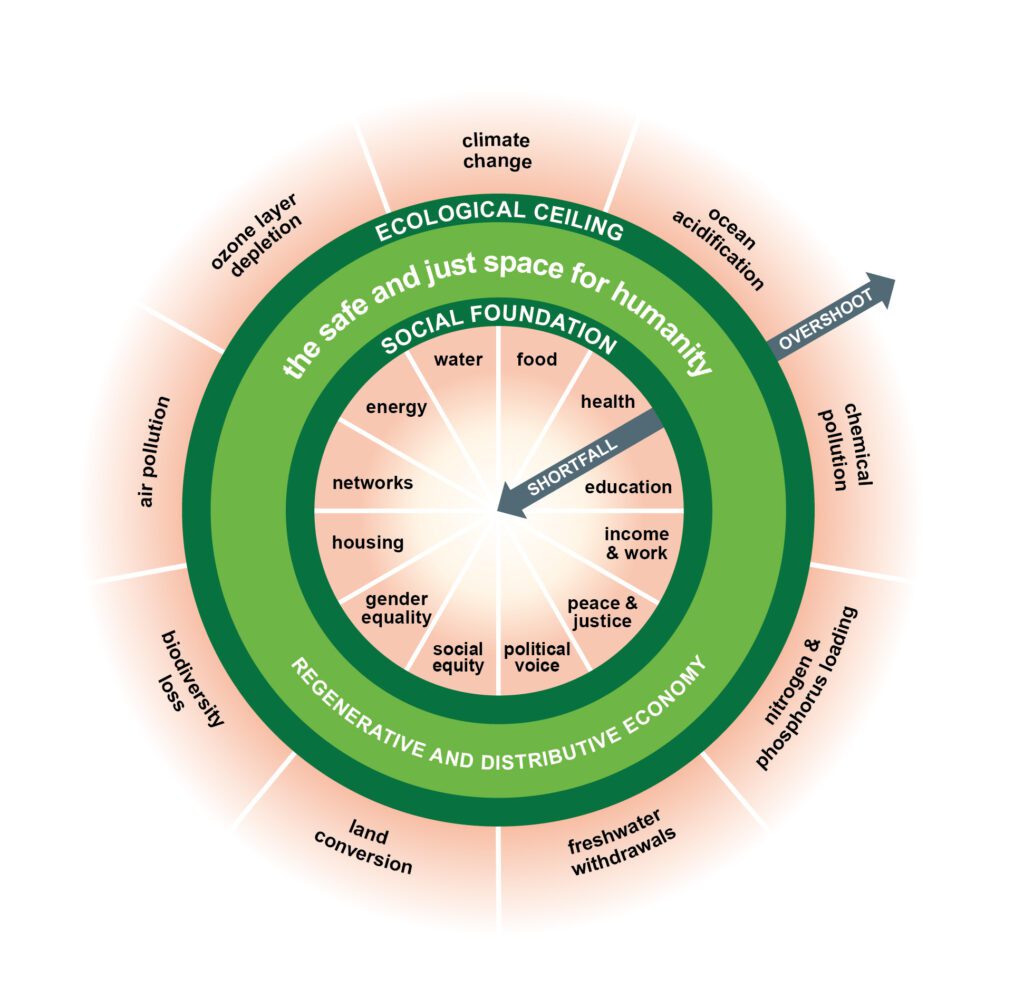
Figure 2: https://www.kateraworth.com/
Once an ecosystem has passed its threshold it can no longer revert back to its original state. We are pressuring a number of ecosystems beyond their functional capacity and are exacerbating our anthropogenic impact on the environment exponentially. This is why we, as a collective, need to rise to the challenge of changing our behaviour in order to ensure our actions and choices promote sustainability so that we can preserve the planet and all the creatures who call it home.
References
- ’Souza, G,D., Cyphers, D., Phipps, T, 1993 . Factors Affecting the Adoption of Sustainable Agricultural Practices. Agricultural and Resource Economics Review, pp. 179-165.
- Daily, B, F., Huang, S, 2001. Achieving sustainability through attention to human resource factors in environmental management. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21(12), pp. 1539-1552.
- Dietz, T., PNAS. Understanding environmentally significant consumption. [Online] Available at: www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1403169111[Accessed 22 April 2015].
- Elbehri, A., Segerstedt, A., Liu, P , 2013. Biofuels and the sustainability challenge:A global assessment of sustainability issues, trends and policies for biofuels and related feedstocks, Rome, Italy: Office of Knowledge Exchange.
- Goodland, R., 1995. The Concept of Environmental Sustainability. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, Volume 26, pp. 1-24.
- Kemp, R., 1994. The problem of technological regime shifts. Technology and the transition to environmental sustainability, 26(10), pp. 1023-1046.
- Scanlan, S. J., 2001. Food Availability and Access in Lesser-Industrialized Societies: A Test and Interpretation of Neo-Malthusian and Technological Theories. Sociological Forum, 16(2), pp. 231-261.
- Urdal, H., 2005. People vs. Malthus: Population Pressure, Environmental Degradation, and Armed Conflict Revisited. Peace Research, 42(4), pp. 417-434.
- van den Besselaar, P., Heimeriks, G, 2001. Disciplinary, Multidisciplinary, Interdisciplinary – Concepts and Indicators -. Scientometrics and Informetrics, pp. 1-9.
- Webersik, C., Wilson, C, 2008. Environment for African Development: A Sustainable Future through Science and Technology, Japan: United Nations University.
- Woodwell, G. M., 1991. The Threshold Problem In Ecosystems, United States: United States Atomic Energy Commission.
- Anand, S. J. (2013). Global Environmental Issues. Open Access Scientific Reports, 1-9.
- Atkin, E. (2013, December 4th). Can A Gym That Converts Workout Energy to Electricity Produce Meaningful Efficiency Benefits? Retrieved from Think Progress: https://thinkprogress.org/can-a-gym-that-converts-workout-energy-to-electricity-produce-meaningful-efficiency-benefits-895c6ae6af68/
- Anand, S. J. (2013). Global Environmental Issues. Open Access Scientific Reports, 1-9.
- Atkin, E. (2013, December 4th). Can A Gym That Converts Workout Energy to Electricity Produce Meaningful Efficiency Benefits? Retrieved from Think Progress: https://thinkprogress.org/can-a-gym-that-converts-workout-energy-to-electricity-produce-meaningful-efficiency-benefits-895c6ae6af68/
- Gelsdorf, K. (2010). Global Challenges and their Impact on International Humanitarian Action. OCHA Policy Development and Studies Branch, 1-21.
- Goodland, R. (1995). The Concept of Environmental Sustainability. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 26, 1-24.
- Moore, P. (2015, April 1st). Technology & Innovation: The fat-burning and energy-producing gyms. Retrieved from The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.com/sustainable-business/2015/apr/01/the-fat-burning-and-energy-producing-gyms
- Sovacool, B. K. (2014). Environmental Issues, Climate Changes, and Energy Security in Developing Asia. Asian Development Bank, 1-30.
- Webersik, C., Wilson, C. (2008). Environment for African Development: A Sustainable Future through Science and Technology. Japan: United Nations University. International Institute for Sustainable Development (Website): Who are the green consumers?




